Oxygen Delivery Devices And Flow Rates Pdf
Pediatric oxygen delivery system oxygen hood covers only head allowing access to the lower body. The oxygen saturation shall be above the target

Pdf Oxygen Therapy For Acutely Ill Medical Patients A Clinical Practice Guideline
A minimum of 6 l/minute of oxygen flow is needed 2to prevent rebreathing of exhaled carbon dioxide.
Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates pdf. Delivery devices work with different flow rates. The patient draws in room Table 3.2 guidance on oxygen delivery devices disclaimer:
A pressure reading (barometer) displays the remaining oxygen pressure in the The flow rate can be set on the wall tap: Prompt clinical assessment is required if oxygen therapy needs to be initiated or increased due to a falling saturation level.
A simple face mask can deliver 35% to 60% oxygen with an appropriate flow rate of 6 to 10 l/minute. There is strong evidence that use of pulse oximetry and the availability of reliable oxygen sources in district and provincial hospitals can reduce death rates from pneumonia by about one third (4). Follow manufacturer’s recommendations (on the air entrainment device) for appropriate flow rates to deliver a specific fio 2.
22% to 60% oxygen with appropriate oxygen flow rates of 0.5 to 2 l/minute. Ideal for short term use for neonates and infants. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates are important concepts to understand as a nurse.
This table is intended to provide information from the technical point of view about oxygen delivery devices, including flow rate ranges, achievable fio 2, and possible oxygen delivery typical flow devices (single use) rate range oxygen sources that can be used with each device. Step up from nasal cannula but doesn’t deliver specific % of oxygen like venturi. Oxygen delivery devices delivery device minimum to maximum liter flow range (adults) approximate o2% delivered notes rt assistance recommended for liter flows of 6 liters/minute or more!
The hudson mask showed evidence of deterioration of performance as the respiratory rate increased both at tidal volumes of 300 ml and 500 ml. • low flow device • most common device used for mild hypoxia • can be set between 1 and 6 lpm (24% to 40% fio2) • fio2 increases approximately 4% with each liter of o2 korupolur gj, needham dm.contemporary criticalcare. Oxygen delivery systems in hospitals and small health facilities.
Flow is a variable describing the movement of a volume of gas over a period of time (l/min). Give an example of each. When the tap is manually opened, the oxygen takes the line of least resistance to the patient via an oxygen delivery device (e.g.
Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates should be adjusted to keep the oxygen saturation in the target range. O2 and air premixed passed through heated humidifiers. Whether your patient is on chronic oxygen, or whether they are in acute respiratory failure , your patients will commonly have oxygen ordered and it will be up to you as the nurse.
If a flow greater than this is used, it is uncomfortable for the child and can cause drying and potential bleeding of the nasal mucosa. The % of oxygen delivery depends on the flow rate and the delivery device. Will deliver total flow to patient approximately 45 lpm.
2009;6(9):1‐11 bailey p, thomsen ge, spuhler vj, et al.crit care med.jan2007;35(1):139‐145. Low flow devices such as nasal cannulas, simple face masks, and reservoir masks deliver oxygen at rates below the normal patient inspiratory flow rate of about 30 liters/minute. Used to deliver oxygen directly into the nostrils to a maximum flow rate of 2 litres per minute.
High flow nasal prong therapy (hfnp) see the hfnp nursing clinical guideline for more information. Nasal cannula 1 0.24 2. Oxygen devices and delivery systems of oxygen flow rate provided, in l·min−1.
Tube with a mask or nasal cannula). Reduction and discontinuation of oxygen therapy • oxygen therapy shall be reduced and discontinued in stable patients with satisfactory oxygen saturation. Oxygen should be prescribed and a signature should be entered on the drug chart on each drug round.
This manual focuses on the clinical aspects of oxygen therapy in children in health Draw gas from bag & ? At a respiratory rate of 10 breaths.min −1, the mask delivered a mean eioc of 94.67% and 88.33% at 15 l.min −1 oxygen flow rate for tidal volumes of 300 and 500 ml, respectively.
The percentage of oxygen inspired depends on the flow rate and the delivery device; Below is an image of the fisher and paykel optiflow nasal cannula junior range for airvo 2. Weaning and discontinuation of oxygen.
Minute ventilation (mv) = vt x rr and peak inspiratory flow rate (pifr) is essentially how fast you draw your breath in, which will be influenced by your mv (if your rr t, your pifr (flow rate) will also t). Estimating fio2 o2 flow rate fio2 o2 flow rate fio2 o2 flow rate fio2. Why is the minimum flow rate of 5 l/min recommended for oxygen delivery by mask?
For details about low flow and high flow devices, see a closer look at some oxygen delivery devices.

Florali The Bottom Line

Evaluation Of Five Oxygen Delivery Devices In Spontaneously Breathing Subjects By Oxygraphy - Waldau - 1998 - Anaesthesia - Wiley Online Library

Oxygen Therapy Obgyn Key
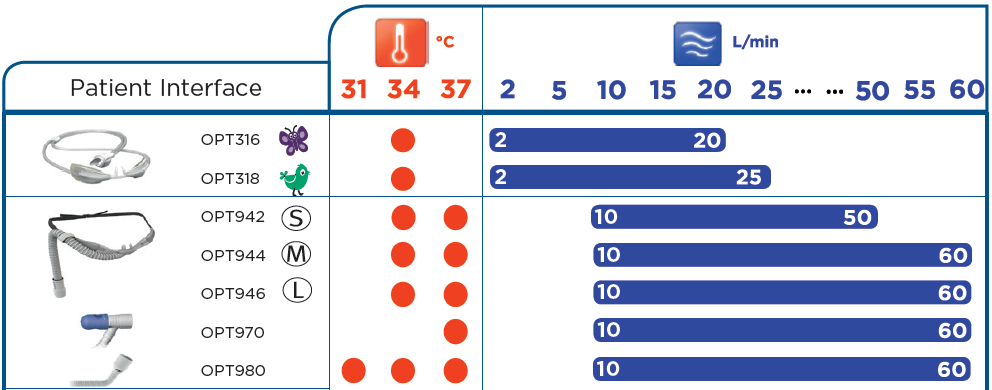
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Pin On Fundamentals Of Nursing
2
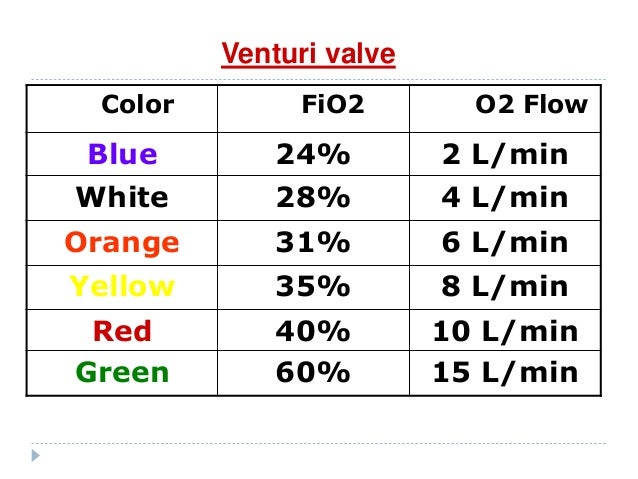
Oxygen Delivery Devices
2
2
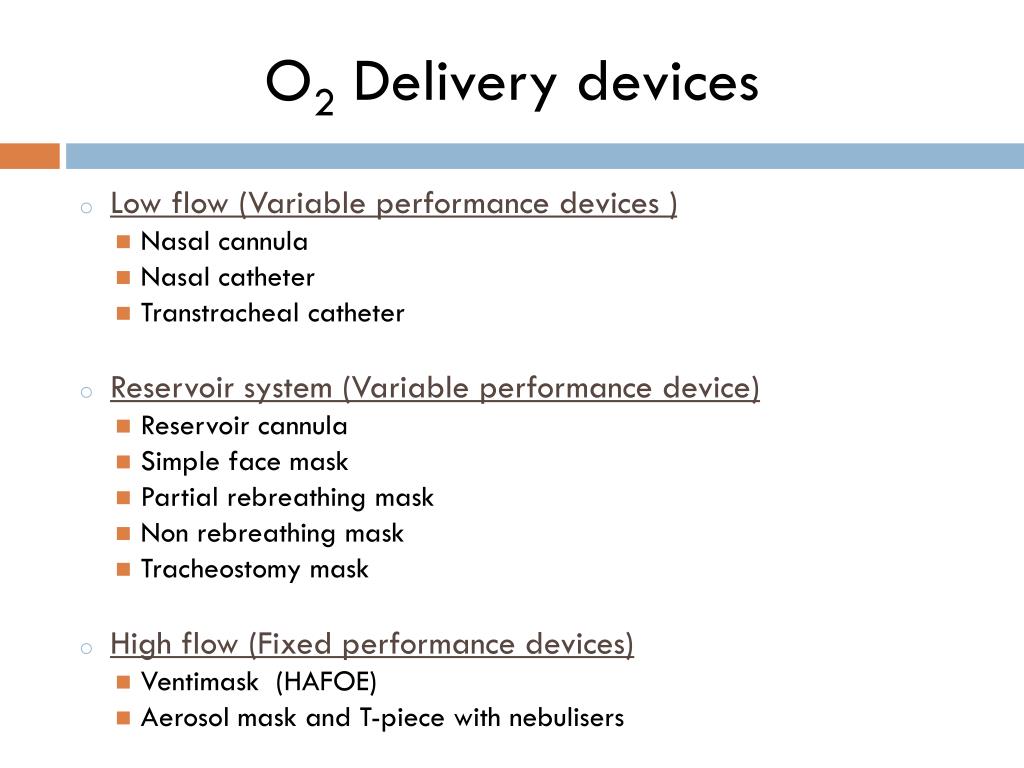
Ppt - Oxygen Therapy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download - Id2942836
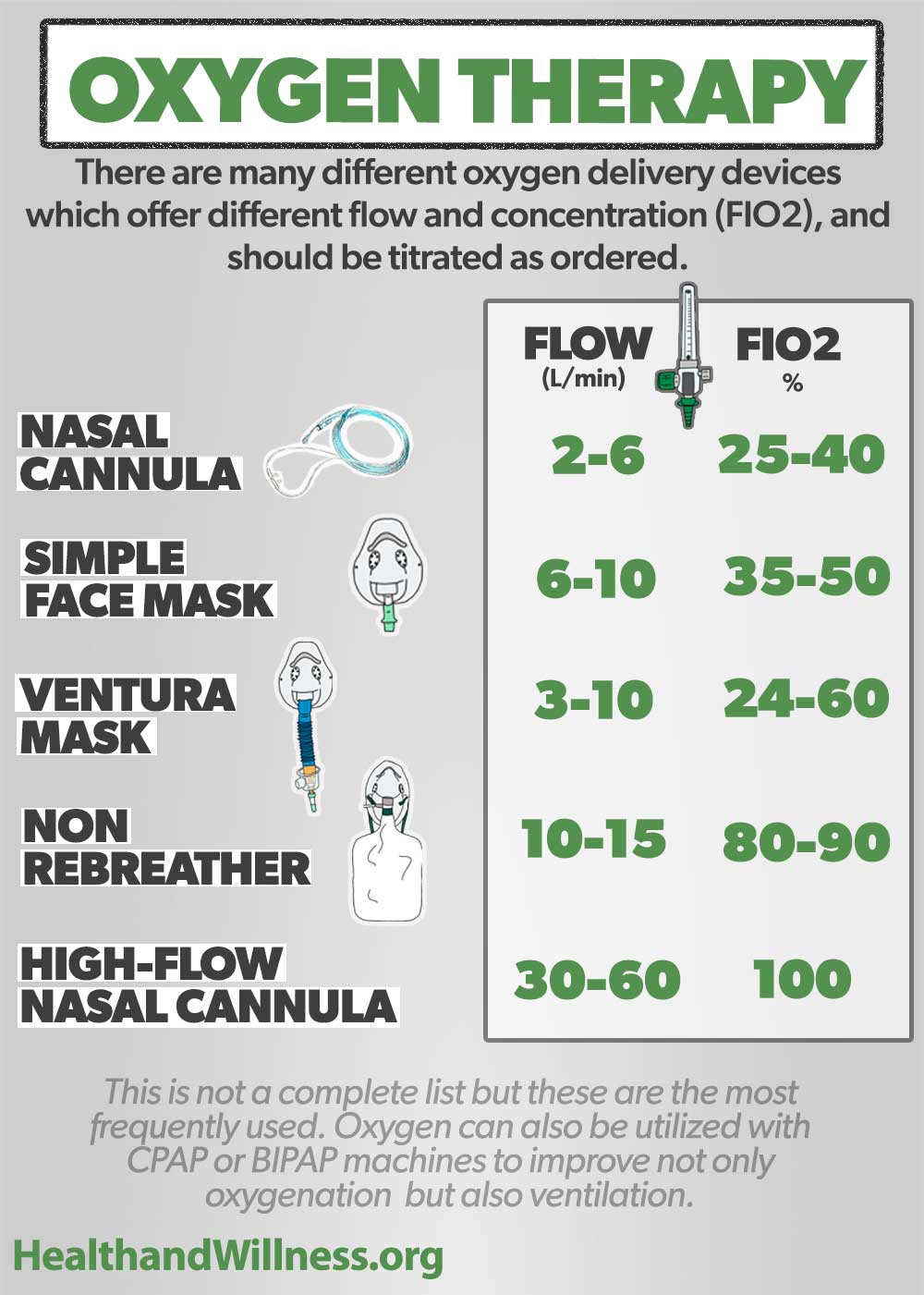
Oxygen Delivery Devices And Flow Rates Health And Willness

Evaluation Of Five Oxygen Delivery Devices In Spontaneously Breathing Subjects By Oxygraphy - Waldau - 1998 - Anaesthesia - Wiley Online Library

Noninvasive Respiratory Support - Emcrit Project

Oxygen Therapy Obgyn Key
2
2
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Pdf Comparison Of The Oxymask And Venturi Mask In The Delivery Of Supplemental Oxygen Pilot Study In Oxygen-dependent Patients Semantic Scholar

Noninvasive Ventilation And Oxygen Delivery Systems